|
英国指导coursework-secondary research-指导英国coursework样本,Lecture 3  Peter Haigh, CEO of Mintel International Group Ltd 2. The nature of desk research n The terms “desk research” and “secondary data search” are used interchangeably by market researchers n Desk research involves ¨consulting and reading documents ¨expert interviews with people who know a particular market place 2. The nature of desk research Primary data = information that is collected for a specific purpose. Secondary data = information that has been previously gathered for some purpose other than the current research project 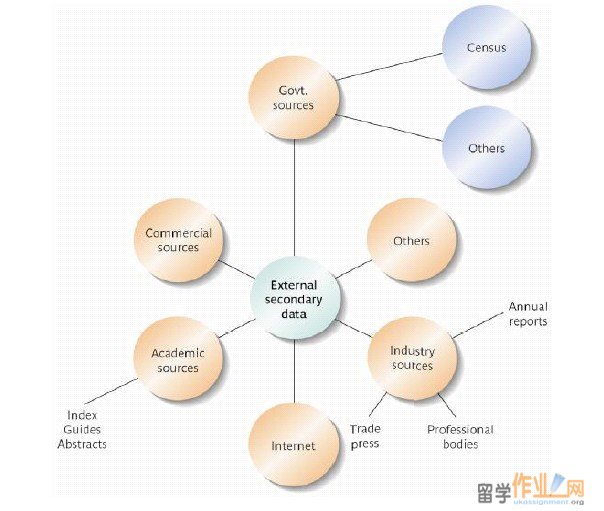 (remember as “second-hand”)3. Uses of desk research n Answer the research question n Help to refine objectives n Help to design primary research n Assist sampling n Supply pre-codes for questionnaires n Help understand results from primary research n Confirm results of primary research n May provide enough information to resolve the problem being investigated n Can be a source of new ideas that can be explored later n Acts as a prerequisite to collecting primary data and can help in designing the primary data collection process Benefits of desk research • Less expensive than primary data • Easy to obtain • Quick to obtain • Useful for international studies • Sometimes more accurate • Sometimes the only way to obtain data Limitations of desk research n May not actually exist n May not be available n May not be accurate n May be outdated#p#分页标题#e# n Will not precisely address the aims / not meet data requirements n Will only provide part of the answer No access to data! The data owner may not want or may not be able to help you. ¨Original records may have been destroyed ¨Records may be in secure locations that are not easily accessible. ¨Storage methods have changed over the years so appropriate apparatus must be available for viewing. e.g. microfiche or 5” floppies 4. Sources of secondary data Different sources Internal secondary data are generated by the organisation in question External secondary data are available in the form of directories, databases, government / industry reports and syndicated services (both on and offline)Freedom of Information n More “internal” secondary data has become available by Freedom of Information laws n Public authorities must make information available through a publication scheme - a document that lists all the different types of information routinely made available n This means the NHS, the Police, publicly owned companies, schools, universities and government, both central and localAppraising Secondary Sources Factors to Be Considered: n Who has collected the data (did they have adequate resources)? n Why was the data collected (how interests of the agency matches with ours)? n How was the data collected (what is the quality of data on-hand)? n What data was collected (geographic and demographic limitations)? n When was the data collected (how old/obsolete is the data)? n Is there consistency? (Aaker, Kumar & Day 2007) Applications of Secondary Data n Demand Estimation n Monitoring the Environment n Segmentation and Targeting n Developing a Business Intelligence System (Aaker, Kumar & Day 2007) Applications of Secondary Data (Contd.) n Census data n Standard Industrial Classification (SIC) n Trade association data n Experts and authorities n Press releases n Legislation and laws n Industry news n Business and practitioner literature, such as magazines Demand Estimation Monitoring the Environment (Aaker, Kumar & Day 2007) Applications of Secondary Data (Contd.) n PRIZM n CLUSTER PLUS n ACORN n DMI n NAICS n TIGER n Competitor’s annual reports n Press releases Segmentation and Targeting Developing a Business Intelligence System (Aaker, Kumar & Day 2007) 5. Search Plan Features n Three approaches are likely: ¨visits to general and specialist libraries ¨contacting human experts ¨carrying out computer searches Features of a plan#p#分页标题#e# You must decide: • time and cost • number of sources • age of sources, • format of data • methodology used Allocate time to: n identify sources n locate sources n secure access to documents n regular progress reports to the client Continuous needs n Set up permanent information requests n Set up intricate delivery formats n Set up on-going news alerts Two needs require different plans. One-off needs n Set up temporary information requests n Use human experts n Plan to stop receiving information Planning The Internet Desk research will start with the Internet so the user must be familiar with ¨directories ¨metasearch engines ¨ search agents Computer-Retrievable Methods n Scope of information available n Speed of information access and retrieval n Commercially available search procedures provide considerable flexibility and efficiency n Rely solely on the accuracy of the abstract author n Depend on the journal and article selection policy of the database producer n Might miss important information, or retrieve a lot of irrelevant data if searching by “keyword” Advantages Limitations (Aaker, Kumar & Day 2007) Assessing the value n To assess the reliability of information look at the source and the context n Use the MR Mix to ascertain the original Purpose, Population used, the Procedure followed and the reason for original Publication. (see example) n For any sector look for the top companies, important trade press titles, trade associations and trade directoriesEvaluation of source and context n Measure reliability and trustworthiness ¨Reliability n Completely reliable; usually reliable; fairly reliable; not usually reliable; unreliable; cannot judge reliability (marks from five though to zero) ¨Trustworthiness 英国指导coursework-secondary research-指导英国coursework样本n Confirmed elsewhere; probably true possibly true; doubtful; improbable; cannot determine the truth (marks from five though to zero) ¨Add marks together, if 6 or more is likely to be usable. If 5 or less, then use with caution (Aaker, Kumar & Day 2007) |
 |
|||
| 网站地图 |

