|
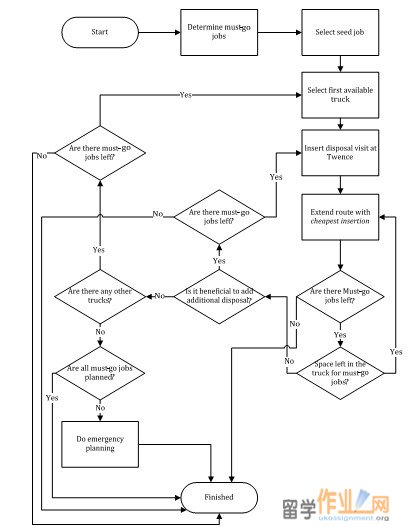
The basic planning heuristic starts with determining a list of must-go jobs. This list includes all containers that are almost full. This is determined by the use of the must-go day, which is a threshold to indicate which containers to empty. The next step in our heuristic is to select a seed job. The seed job is used to create an efficient route. Then we assign this seed job to the first available truck and assign other jobs from the must-go list to the route of this truck. This means we fill one truck before using another. By using only one truck at a time, we try to achieve a high fill rate of the truck. The fill rate is one of the performance indicators and a low fill rate, with a low number of jobs per truck, results in relatively high costs per kilo of collected refuse. The basic planning heuristic consists of several steps to select containers and create a route to empty these containers. Figure shows a flowchart of these different steps we use to make a more dynamic planning methodology.
While extending the route, we have to check whether there is space left in the truck, both in truck capacity as well as in time. If there is space left, another must-go job can be assigned. When there is no space left in the truck, we have to make a decision whether to add an additional disposal trip. This depends on the time of the day. When the day is almost over, it might be a better decision to use a new truck. When we choose for an additional disposal visit, we can then again continue with creating a new sub-route for the truck. When deciding to use another truck, jobs are assigned to this new truck. In case all trucks have already been used, and there are still must-go jobs left, we have to do emergency planning.
According to study the best policy by the American National Standards Institute, principles and technical requirements policy can meet workers' clothing requirements and best practices and policies developed.There are three workers and experienced minimal traffic and safety of higher-level targets of waste. For this algorithm, the average distance traveled was originally 12.2 km. The new route covered by the greedy algorithm application for the best new course in the region is found by the distance of 9 km providing a 25% improvement. This will cut down on time and cost to produce.At last,the random routes of waste collecting can reach at 16.4km.The comparison of distances with different methods are as followed.
Table 1 Comparison of distances with different methods
Route Distance
Algorithm 12.2
Optimal 9
Radom 16.4
Adopted the recommendations of heuristic decline, the number of vehicle service can reach to three or four to complete. To cut back the number of times is enable to run every day. Because of the shorter operating time,it would reduce operating trucks and operating costs and labor can be achieved. In this algorithm, it is easy to pull the car off the road for repair and maintenance helping to extend the life of the vehicle. Heuristic provides a number of recommendations for human insight router. Some parts of the routing tasks can easily be done by a computer while others require judgment and intuition. The new decision-making procedures would make scheduling of solid waste collection routes which will go a long way to solve the chaos dumping levy because it will reduce costs to increase the frequency of the problem of solid waste collection. Solid waste collection vehicle routing efficiency by reducing spending will reduce the cost of labor in the collection. The algorithm provides the best route saving energy and reducing working hours and vehicle fuel consumption. One of the conclusions is that the analysis system can be successfully applied to municipal solid waste management issues. The study shows how a simple heuristic method for decision-makers to provide effective solutions to complex problems in urban waste management. Successful solutions would provide the best solutions to the sensitivity of existing resources laid the foundation for further study .
The research on the current system provides a standard in the purpose of reducing the cost of the element. This goal has been reached to some extent. It may be acceptable to reduce the cost savings by using a relatively simple algorithm to obtain. This paved the way for the future in use of more sophisticated algorithms,which would take into account the capabilities and limitations of time. In conclusion, it would be safe to say that the route which may be considered to be provided the fact that the implementation of the bearing is a great need to study and improve garbage collection system.
The main results are as follows:
• Each load category will require less than 40 samples to determine the load components from residential sources.
• Less than 100 loads will be required to quantify the amount of paper.
Obviously, sorting and weighing has a sufficient number of samples to obtain a reasonably accurate which would estimate of the cost of everything expensive compared to the most common waste composition. Survey design have selected the method which can be used to estimate the accuracy of the resulting data.Please note that such estimates involve representatives of the real situation in the accuracy of investigation related to the accuracy of individual measurements in the equivalent waste on the composition of discussion.
In larger facilities for visual classification it can be economically expanded data set making it possible to improve accuracy.However, this increases the precision assumed to be measured by visual classification which is not prejudiced. In these examples, the result can lead to visual classification threefold increase accuracy.
Appendix Routes on random solutions

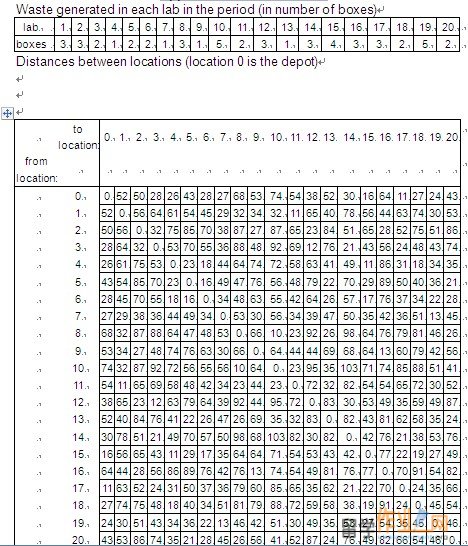
Appendix 2 Data solution
|
 |
|||
| 网站地图 |