|
Assignment 1
星巴克咖啡公司1971年在西雅图成立,它已经成为一个国际化和全球化的咖啡连锁店。在咖啡零售的销售行业里,截至到2007年星巴克已有超过15,000家专卖店遍布世界各地,根据星巴克的材料及案例,我们已经得到SWOT对20世纪的数据分析。此外, 会向星巴推荐一种战略方针,而且从1990年到2007年,也一直在对其做评估。
从国内的角度看,星巴克的优势和劣势都需要考虑,它的第一个优势就是它的高质量,星巴克选择了最好的阿拉比卡咖啡豆,确保咖啡的质量标准,以便向客户提供高质量的咖啡,星巴克直接从原生产国买咖啡,而不是依靠批发商。第二优势是人力资源企业文化,星巴克聘用有天资的人,并培训他们。对于那些工作20个小时或以周以上的员工,会给他们提供医疗保险,这样,它就吸引了那些体格强壮,又愿意致力于提供更好服务的候选人。另外优秀的员工会促进客户与星巴克品牌的关系,第三个优势就是星巴克在特种咖啡市场的拓展。在20世纪90年代初,在洛杉矶,旧金山,芝加哥等城市大量客户开始定期喝星巴克咖啡。此外,星巴克收入暴增,并获得了不少良好的口碑。星巴克的唯一弱点就是由于它肆意的市场拓展而引起的资金问题。在北美,星巴克拥有的零售店并不具有营业执照。它的竞争对手比如西雅图最佳咖啡及第二杯都选择了特许经营,因此需要较少的内部融资来扩张。此外,其他的弱点是品牌稀释。由于在餐厅和飞机上提供的星巴克咖啡多元化,这使星巴克产品的形象边界变得模糊。
Starbucks Coffee was founded in Seattle in 1971, which had become an international company and global coffee-house chain. In the industry of retail coffee-house sales, Starbucks had more than 15,000 stores all over the world by 2007. According to the Starbucks’ materials and cases, a SWOT analysis for mis-1990s will be given. In addition, a strategy will be recommended to Starbucks and be evaluated realized from mid-1990s to 2007.
From the internal perspective, strength and weakness of Starbucks are considered. The first strength of Starbucks in 1990s was its high quality. Starbucks selected the finest Arabica beans to make sure the highest standards of quality coffee offered to customers. Starbucks bought its own coffee direct from producing countries rather than relying on wholesalers. The second strength was human resources corporate culture. Starbucks hired the talented people and training them. Starbucks offered the health-care coverage to all employees who worked 20 hours or more a week. It attracted strong, committed candidates to work and to provide better services. In addition, excellent employees enhanced the relationship between Starbucks brand and customers. The third strength was Starbucks’ expansion of specialty coffee market. Larger number of customer started drinking Starbucks coffee on a regular basis in the early 1990s in LA, San Francisco, Chicago and other cities. Furthermore, Starbucks boomed revenues and earned a lot of good reputation. One of Starbucks weakness in the 1990s was the financial problem caused by its aggressive expansion. In North America, Starbucks owned all of its retail outlets instead of licensing arrangement. However, Starbucks depended heavily on equity and debt financing to expand. Its competitor like Seattle’s Best Coffee and the Second Cup all chose franchising and thus need less internal financing to expansion. Furthermore, the other weakness was brand dilution. Due to the diversification of the products such as providing Starbucks coffee in restaurant and airplane, it made the image of Starbucks products boundary indistinct.
From the external perspective, the opportunities and threats existed simultaneously. One opportunity of Starbucks in the 1990s was the growth demand for specialty coffee. Besides,new distribution channel provided opportunity to get more customers. For example, the shopping mall, grocery, and international market were an area of opportunity for locating coffee house and it had high rate of coffee consumption. Coffee house in these place not only provided coffee drinks but also was a break place. Starbucks also launched a new American online cafe store to become a global company. However, the threat of Starbucks in the 1990s mainly came from the growth of major coffee-shop competitors, which were franchisers and operating risk at the store level, like Second Cup. Substitutes such as tea, juice, soft drinks, and other coffee and non- coffee-related drinks, compete with the Starbucks as well. Nevertheless, the consumption of specialty coffee was not declining significantly due to these substitutes.
By synthesizing the OT and SW factors, strategic options that help Starbucks create and capture value are suggested in the SWOT synthesis table below.

Most of the existing strategies of Starbucks in the 1990s fitted with the SWOT synthesis table according to the case ‘Trouble Brews at Starbucks’. For example, in terms of different distribution channels, Starbucks took the grocery market into consideration and succeed in testing market in Portland area. Starbucks also began to do some national advertising. In addition, to maintain the service and atmosphere competitive, Starbucks tailored special logo and vision to provide coffee bars with Italian culture, romance and mystery. Starbucks also expanded their business model which was a stronger connection with customers as the Third Place. Seasonal offering, such as cream Frappuccino in the summer and gingerbread latte at Christmas in certain stores, were introduced as production localization and diversification. Starbucks lowered the financial risk through licensing with airport retail and partner with Safeway, and Barnes & Noble. It gave Starbucks a way of entering new markets without affording to build company- own stores.
To some extent, partnering with McDonald was not contribution to the image of Starbucks brand. Mc Donald is a fast food restaurant where the environment is noisy. Thus it is paradox of the Starbucks’ marketing culture. It may cause the brand dilution for Starbucks and it is actually a negative way of promotion of Starbucks.
作业 Assignment 2
根据卡普兰和诺顿(2007),平衡计分卡(BSC)是一个使用的财务指标和非财务指标来监控作业进度混合物的战略绩效管理工具,最近平衡计分卡已经发展成为一种有效的战略执行框架,它可将组织的愿景和战略转化为经营目标和绩效。它包括四个方面,即财务,客户,内部业务流程,学习与成长。平衡计分卡应用到凯普斯仿真,使重要的战略得以实现。
According to Kaplan and Norton (2007), Balanced Scorecard (BSC) is a strategy performance management tool which using a mixture of financial measures and non-financial measures to monitor operation progress. Recently, the BSC has evolved to become an effective strategy execution framework that transforms an organization’s vision and strategy into operational objectives and performance. It consists of four perspectives, namely financial, customer, internal business process, and learning and growth. BSC is applied in Capstone simulation to achieve the key’s strategies.#p#分页标题#e#
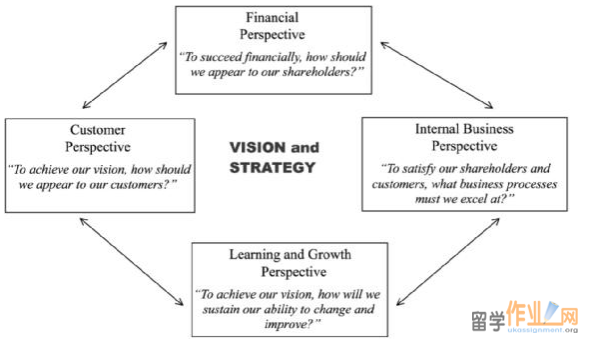
In Capstone simulation, the key strategy of our Digby group was broad differentiation. We maintained a presence in every segment of the market. Thus, BSC measured performance across four categories to translate the vision and linked them to a strategic management system.
In financial aspect, we charged a relative high price in high-end, performance, size and traditional products since we differentiated our products. Meanwhile, we charged a relative low price in low-end products through getting large market shares and low costs to generate a high profit. In addition, leverage was also utilized in this perspective, which required balancing between the equity and debt. In customer aspect, examining the preference of customer in each segment, we developed R&D frequently to keep our design advanced and improved the production line or price adjustment to meet customers buying criteria. Besides, we largely invested in the promotion budget and strengthened our distribution channels to achieve customer awareness and accessibility. For example, in high-end analysis, customer buying criteria is ideal position, age, reliability, and price in sequence. The internal business process and customer perspectives can cross-check performance. In internal business process aspect, profit is indicated by contribution margin, the contribution margin of our group is certain high due to high price and low costs. We also focused on plant utilization to avoid paying depreciation and interest on underused assets. Specially, within a plant utilization range of 100% - 180%, we are deemed to be working our assets productively. In learning and growth aspect, it was a measure to evaluate employee productivity. Strategic learning consists of link individual efforts, job satisfaction and gathering feedback. For Capstone simulation, we cannot gather the employees’ satisfaction and feedback. We connect Training, Turnover and Total Quality Management (TQM) to measure productivity alone. For instance, because of requiring high R&D, we decided to invest on the TQM to increase the speed of R&D.
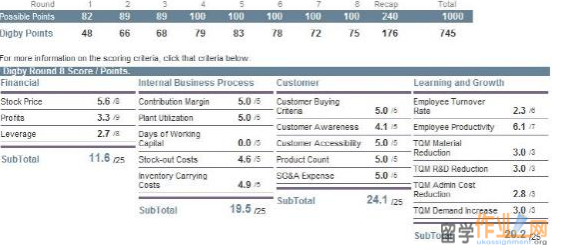 . .
Picture 1, souring from the Capstone Simulation
We evaluated the performance in each round according to the score in Balanced Scorecard points. Take an example in Picture 1 above, souring from the Capstone website Digby. In round 8, in financial perspectitive, the profit was only 3.3 point and the leverage was 2.7 point. So the sales, costs and the strcuture of capital was the issue. We should pay attention to this part. However, in our simulation, the profit was failure because of the lowest price and small market share.
Assignment 3
凯普斯通模拟市场在这八轮的演练中一直在改变,涉及市场需求,产品定位,以及客户可访问性等。在六家公司之间为五个阶段产品竞争。因此,为了得到在凯普斯行业可持续的竞争优势,竞争战略是公司必不可少的。然而,在凯普斯模拟,避免强大的竞争似乎并不容易。因此,在凯普斯行业的任何公司是不可能采用以蓝海策略的。
The Capstone simulation market was changing all the time in these 8 rounds, involving the market demand, the product position, and customer accessibility and so on. The competition of the five segments products occurred among six companies. So, in order to get sustainable competitive advantages in Capstone industry, the competitive strategy is essential for the company. However, in Capstone simulation, avoiding the strong competition seems not easy. So, adopting to the Blue Ocean strategy is impossible in Capstone industry for any firm.
The Round 8 total market demand and each company’s market share have been depicted on Figure 1. In the final round, it is significant that each company had its own target product vision. For example, Erie Company focused on performance products, and in this segment they had two products. In my company, Digby, we developed three products in size, and occupied more than 30% market share. Almost all companies focused on the high-end products, and each company had more than two series of products in high-end position. R&D was essential in high-end products, so the competition and investment were drastic and huge.
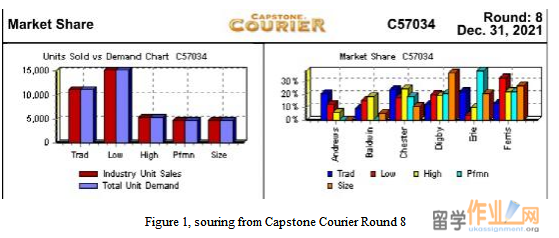
Figure 1, souring from Capstone Courier Round 8
The strategy in Capstone is to earn the core competence such as differentiation, lower cost and operational effectiveness. However, Porter (1996) argued that the sustainable advantage was different from operational effectiveness. The operational effectiveness is necessary but not sufficient. The company can get operational effectiveness only if differentiation itself outperforming the rivals. So the functional strategy becomes important, which is the approach to achieve corporate and business unit objectives and strategies by maximizing resource productivity. Capstone functional strategy involved the R&D strategy like innovation, marketing strategy like 4P, operational strategy like automate assembly line, and HRM strategy like training. To succeed in Capstone simulation, we can control all these factors, and utilize these strategies to achieve the large market shares and profit. For example, in the first round, we invested a lot in marketing promotion to get product high awareness and accessibility. In addition, the R&D investment ensured the products position and automate investment lower the labor costs.
According to Kim and Mauborgne (2004), blue ocean strategy is doing the business avoid competition and create new opportunity. Finding the new market can be achieved by two methods. One way is creating new industry which means exploring the new segment customers. The second way is to make a new blue ocean from within the red ocean, which represents breaking through the boundary traditionally. However, it is almost impossible to implement a blue ocean strategy in Capstone Simulation. Due to the certain customer segments and optimal products position had been given in advance, our company only need to meet the customer demand instead of creating new customer group and industry. The Capstone simulation is a red ocean, which we cannot avoid competition.
|
 |
|||
| 网站地图 |

